How are PVC and Polypropylene or Polyethylene barriers different?
 By
Alana Graham
·
2 minute read
By
Alana Graham
·
2 minute read
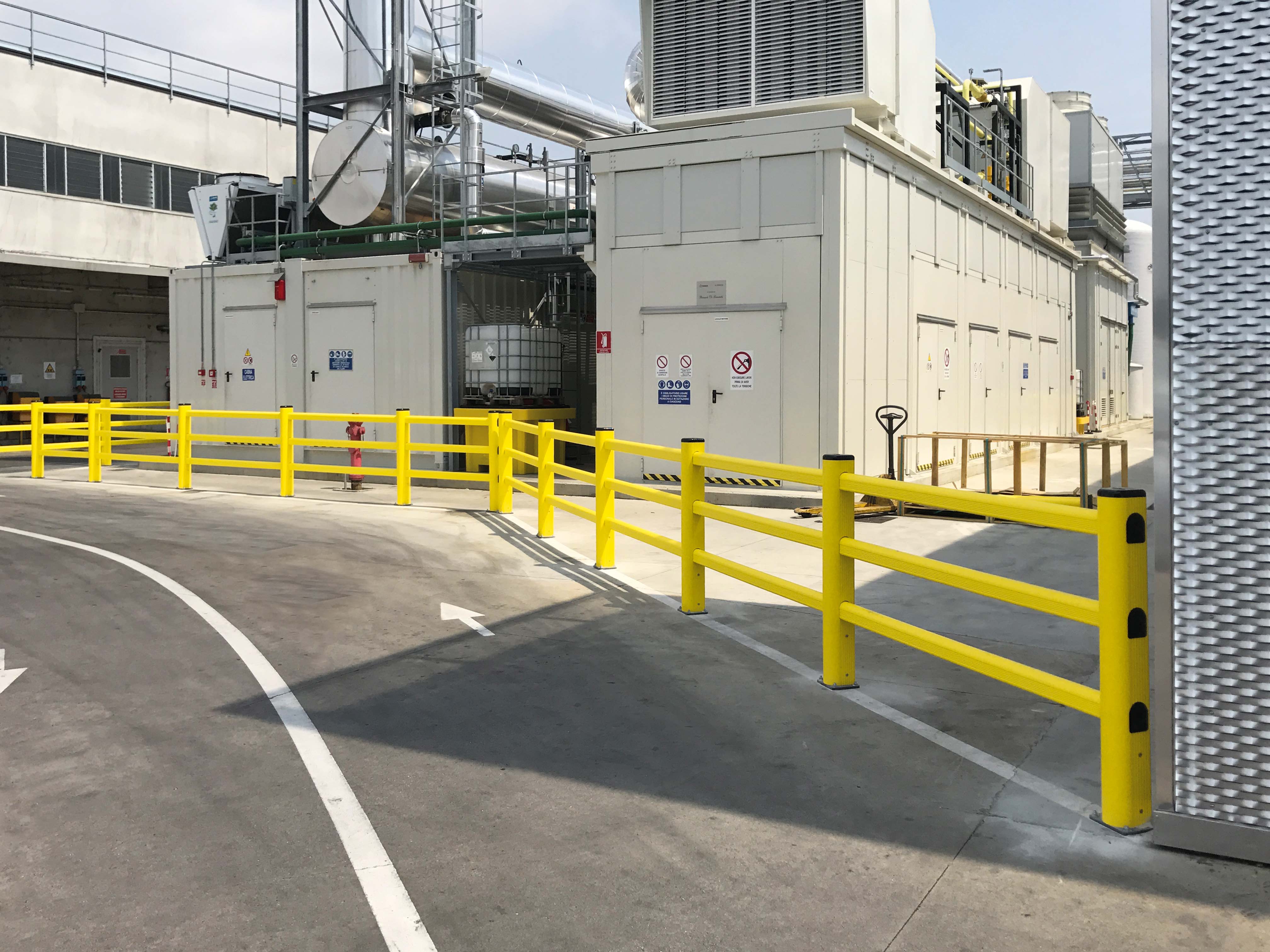
If you have read our (how to choose the right barrier for me) article, you likely are needing more information about the different options of polymer barriers. It can be hard to know the differences between different types of polymers, let alone in the form of a barrier.
In this article you will learn the differences between PVC, polypropylene, and polyethylene barriers, highlighting key features and benefits so that you can make an informed decision on which to buy in your factory.
Contents:
- Flexibility and Impact Resistance
- Functional Design and Shock Absorption
- Shock Absorber Efficiency
- Scratch Resistance
- Installation Ease
- Sectional Adjustability
- Cleaning Convenience
- Space Efficiency
- Fire Resistance
- Summary Table
Flexibility and Impact Resistance
- PVC: Exhibits high elasticity, returning to its original shape after it is hit.
- Polypropylene and Polyethylene: Tend to lose colour and suffer more deformation under stress.
Functional Design and Shock Absorption
- PVC: Features a wide, flat impact surface, effectively preventing forklifts from slipping underneath.
- Polypropylene and Polyethylene: Often have cylindrical shapes, posing a risk of forklifts slipping under or over them.
Shock Absorber Efficiency

- PVC: Utilises three soft shock absorber areas for superior impact absorption.
- Polypropylene and Polyethylene: Typically have minimal or rigid, non-absorbing materials.
Scratch Resistance

- PVC: Fully pigmented and resistant to scratches, with a specially treated surface.
- Polypropylene and Polyethylene: Only have a pigmented upper layer, making scratches visible and difficult to conceal.
Installation Ease
- PVC: Can be installed in three simple steps.
- Polypropylene and Polyethylene: Require numerous components, leading to time-consuming assembly.
Sectional Adjustability
- PVC: Comprised of uniform pieces, allowing for easy extension or shortening post-installation.
- Polypropylene and Polyethylene: Require complete disassembly to modify initial and final posts.
Cleaning Convenience

- PVC: Easy to clean with just water.
- Polypropylene and Polyethylene: Tend to absorb dirt, making them hard to clean.
Space Efficiency 
- PVC: Compact design requires minimal space from shelves.
- Polypropylene and Polyethylene: Need larger dimensions and more space to provide equivalent protection.
Fire Resistance
- PVC: Rated V0 for self-extinguishing properties.
- Polypropylene and Polyethylene: Are rated HB (Horizontal Burn), thus burning readily in case of fire.
PVC offers significant advantages in flexibility, scratch resistance, shock absorption, and fire resistance compared to polypropylene and polyethylene, making it a superior choice for industrial protection. Read about the fire ratings here.

When you are choosing a partner to work with to implement flexible polymer barriers at your site, it is important to find out what their barriers are made from to ensure you are finding right barrier based on the properties you need it to have at your site. Read the article here to find out more about how to choose the correct barrier for your site.
You should now have a greater understanding of the properties of polymer and metal barriers so you are able to make your own informed decision. If you would like to speak to an expert to discuss your options, please get in touch here.